Instruction for Neurobion injections
You can buy Neurobion injections here
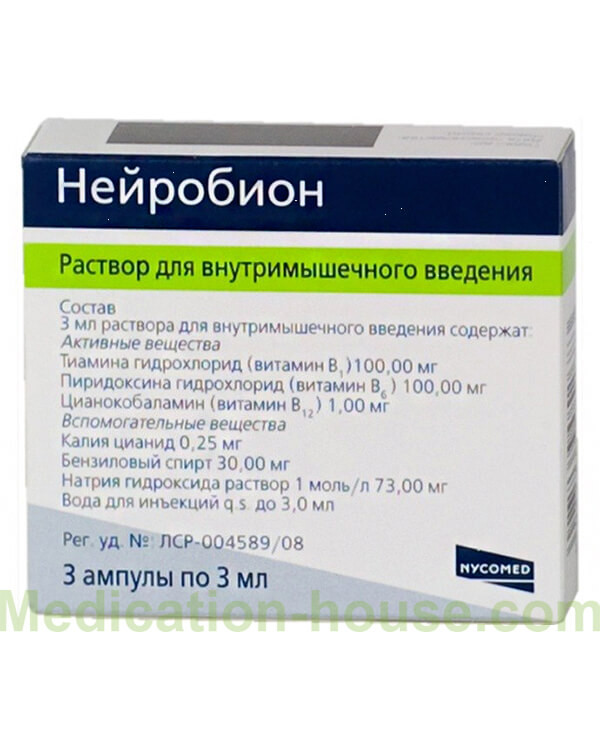
Composition
3 ml of the solution for intramuscular injection contain:
Active substances:
Thiamine hydrochloride (vitamin B1) 100.00 mg
Pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6) 100.00 mg
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) 1.0 mg
Excipients:
potassium cyanide 0.1 mg, sodium hydroxide solution 1 M 73.0 mg, water for injection to 3 ml.
Pharmacodynamics
Neurobion injections contains a combination of neurotrophic active substances of the B complex of vitamins. The vitamins contained are thiamine (B1), pyridoxine (B6) and cyanocobalamin (B12) play a special role as coenzymes in the intermediate metabolism that occurs in the central and peripheral nervous system.
A special role in the metabolic processes of the nervous system is played by the combined effect of vitamins B1, B6 and B12, which justifies their combined use. The combined use of B vitamins accelerates the regeneration of damaged nerve fibers. It has been proven that the effectiveness of a combination is superior to that of a single component.
Like other vitamins, they are essential nutrients that the body cannot synthesize on its own.
The therapeutic introduction of vitamins B1, B6 and B12 into the body replenishes the often existing insufficient intake of vitamins from food, which ensures the presence in the body of the necessary quantities of coenzymes.
The therapeutic use of these vitamins in various diseases of the nervous system is aimed, on the one hand, to compensate for the existing deficit (possibly due to an increased need of the body caused directly by the disease) and, on the other hand, to stimulate natural mechanisms aimed at restoring the function nerve tissue.
However, the indirect analgesic effect of the B complex of vitamins has a beneficial effect on the therapeutic outcome.
Pharmacokinetics
Thiamine
After ingestion, thiamine undergoes dose-dependent transport, the mechanism of which is dual in nature: active absorption at concentrations up to 2 µmol / l and passive diffusion at concentrations above 2 µmol / l. Thiamine phosphorylation occurs in the liver. The half-life is about 4 hours. The human body contains about 30 mg of thiamine. With the rapid metabolism, it is displayed in 4-10 days.
The half-life is about 4 hours.
The human body contains about 30 mg of thiamine. With the rapid metabolism, it is displayed in 4-10 days.
Pyridoxine
The human body contains about 40-150 mg of pyridoxine. 1.7-3.6 mg per day by the kidneys.
Cyanocobalamin
Excess cyanocobalamin mainly accumulates in the liver. The daily need for vitamin is 1 mg.
The metabolic rate of cyanocobalamin per day is 2.5 μg, or 0.05% of the amount found in the liver.
From the liver, it is excreted with bile into the intestine and is largely reabsorbed by the enterohepatic circulation.
Indications for use
In the treatment of the following neurological diseases:
Neuropathic pain caused by polyneuropathy (including diabetic and alcoholic);
Neuritis and neuralgia:
trigeminal neuralgia,
neuritis of the facial nerve,
intercostal neuralgia,
pain syndrome caused by diseases of the spine (lumboischialgia, plexopathy, radicular syndrome caused by degenerative changes in the spine),
herpes zoster.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any component of Neurobion injections.
Childhood.
Pregnancy
The use of Neurobion injections is not recommended, due to the lack of data on the use during pregnancy.
Lactation
Vitamins B1, B6 and B12 are excreted in breast milk, but the risk of an overdose in a newborn has not been established. In some cases, taking high doses of vitamin B6 (> 600 mg per day) may suppress the secretion of breast milk.
If necessary, taking Neurobion injections during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Dosage and administration
Neurobion injections is administered intramuscularly (deep injections into the gluteus maximus muscle).
Treatment is recommended to begin with the intramuscular injection of 1 ampoule (3 ml) per day until the removal of acute symptoms.
After improvement of symptoms or in cases of moderate severity of the disease: one ampoule 1-3 times a week for 2-3 weeks.
For maintenance therapy, for the prevention of recurrence, or for the continuation of the course of treatment, the drug Neurobion injections is recommended in another dosage form (coated tablets).
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Side effect
The frequency of side effects of Neurobion injections is as follows:
Very frequent:> 1/10
Frequent:> 1/100, <1/10
Frequent:> 1/1000, <1/100
Rare:> 1/10 000, <1/1000
Very rare: <1/10 000, including individual messages
Frequency is not installed: can not be estimated with available data.
Nervous system disorders:
Frequency not established: long-term use (> 6-12 months) of vitamin B6 in a daily dose of> 50 mg may cause peripheral sensory neuropathy.
Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract:
Frequency is not installed: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
Immune system disorders:
Very rarely: hypersensitivity reactions such as sweating, tachycardia, skin reactions (itching, urticaria), anaphylactic shock.
General disorders and disorders at the site of administration:
Frequency not established: reactions at the site of administration.
Overdose
Vitamins B1, B6 and B12 have a wide therapeutic range. Symptoms of overdose are not observed when using Neurobion injections in recommended doses and regimen. With intravenous administration of high doses of vitamins for a long time (more than 2 months) symptoms of intoxication may be observed.
Vitamin B1: after administration of a dose exceeding the recommended one more than 100 times (> 10 g), curare-like ganglioblokiruyuschie effects were observed, causing a violation of the conduction of nerve impulses.
Vitamin B6: prolonged use (> 6-12 months) of vitamin B6 in a daily dose of> 50 mg may cause peripheral sensory neuropathy.
Prolonged use of vitamin B6 in a daily dose of more than 1 g for more than 2 months can cause neurotoxic effects.
After the introduction of more than 2 g per day, cases of hypochromic anemia and seborrheic dermatitis, neuropathy with ataxia, sensory disturbances, epileptiform seizures with changes on the electroencephalogram were described.
Vitamin B12: after parenteral administration of a high dose, eczematous skin disorders and a benign form of acne were observed.
In the event of the above symptoms of overdose, treatment with Neurobion injections should be discontinued. If necessary, symptomatic therapy is prescribed, including desensitizing.
Interaction with other drugs and food
With simultaneous use, pyridoxine may reduce the anti-Parkinsonian effect of levodopa.
The simultaneous use of pyridoxine antagonists (for example, isoniazid, hydralazine, penicillamine, or cycloserine) may increase the need for pyridoxine.
“Loopback” diuretics, for example, furosemide, can block tubular reabsorption, thus enhancing the excretion of thiamine with prolonged use, which leads to a decrease in the content of thiamine in the blood.
It is not recommended to mix Neurobion injections with other drugs in the same syringe.
Vitamin B1 is completely destroyed when interacting with solutions containing sulfites.
special instructions
Neurobion injections should not be administered intravenously.
The clinical picture, as well as laboratory tests with funicular myelosis or pernicious anemia, may lose their specificity when vitamin B12 is administered.
Influence on ability to drive and work with mechanisms
Neurobion does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and to control mechanisms.
Storage conditions
At a temperature not higher than 8 ° C in a dark place.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life - 3 years.
Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package.
Terms of sell
You don't need a prescription to buy Neurobion injections.