Pyridoxine hydrochloride instruction
You can buy Pyridoxine hydrochloride here
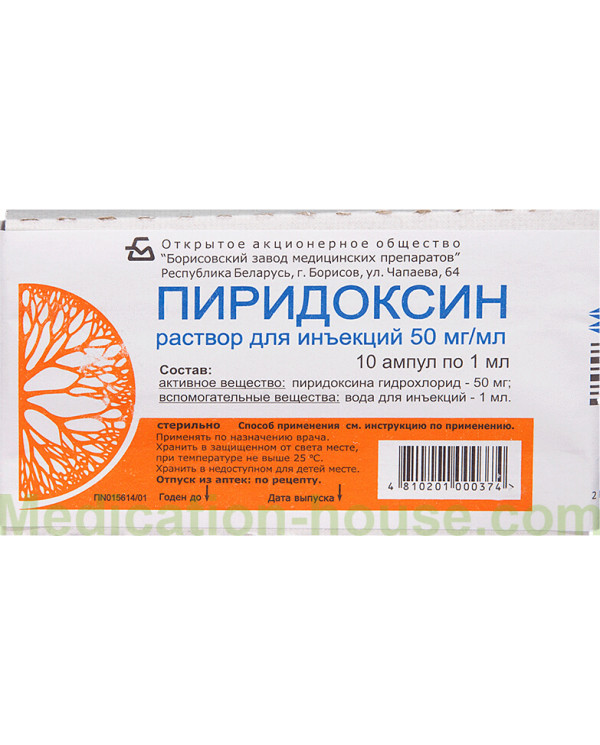
Composition
active ingredient: pyridoxine;
1 ml of pyridoxine hydrochloride 50 mg
excipients: sodium edetate, water for injection.
Indications
Comprehensive treatment of gestational toxicosis, arteriosclerosis, anemia (including sideroblastic), leukopenia, nervous system diseases (radiculitis, neuritis, neuralgia, parkinsonism, Little's disease), depression, involutional age seboreepodobnyh and neseboreynyh dermatitis, herpes zoster, neurodermatitis, psoriasis, exudative diathesis, when removing from binge and hangover syndrome. It is also prescribed for air and sea diseases, Meniere's disease. Pyridoxine hydrochloride warns or reduces toxic effects (especially polyneuritis) in the treatment of anti-TB drugs. Treatment of pyridoxine basement trial.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the drug. Peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer (due to a possible increase in gastric acidity). Liver disease, occurring with severe functional impairment. Coronary heart disease.
Dosage and administration
The drug Pyridoxine-Darnitsa is administered intramuscularly, intravenously or subcutaneously in cases where oral administration is not possible.
The course of treatment is individual and is determined by the type and severity of the disease.
The solution is prepared immediately before use - a single dose of the drug is diluted in 1-2 ml of water for injection or 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Adults
Hypovitaminosis B 6: the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 50-100 mg (1-2 ml) for 1-2 administrations. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks.
Sideroblastic anemia: the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 100 mg (2 ml) 2 times a week. It is also recommended to take folic acid, riboflavin, vitamin B 12).
Depression of the involutionary age: the drug is prescribed at a dose of 200 mg (4 ml) per day. The course of treatment is 20-25 injections.
The use of drugs of the isoniazid group: the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 5-10 mg (0.1-0.2 ml) during the entire course of treatment with isoniazid.
Overdose of isoniazid preparations: for every 1 g of overdose preparation, 1 g (20 ml) of pyridoxine is administered at a rate of 0.5 g / min. With an overdose of isoniazid, more than 10 g of pyridoxine is administered intravenously at a dose of 4 g (80 ml), and then intramuscularly - 1 g (20 ml) of the drug every 30 minutes. The total daily dose is 70-350 mg / kg.
Toxicosis of pregnant women: the drug is prescribed in a dose of 50 mg (1 ml) per day. The course of treatment is 10-20 injections.
Pyridoxine-sensible anemia (macrocytic, hypochromic with an increase in the level of iron in the blood plasma): the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 50-200 mg (1-4 ml). The course of treatment is 1-2 months. If there is no effect, they switch to another type of therapy.
Pyridoxinezalezhniya syndrome, including pyridoxinezalezhni spasms: the drug is prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly at a dose of 50-500 mg (1-10 ml) per day. Enter at a rate of 50 mg / min. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks.
Parkinsonism: the drug is prescribed in a dose of 100 mg (2 ml) per day. The course of treatment is 20-25 days. After 2-3 months - a second course. According to another treatment regimen:
the drug is prescribed in the initial dose of 50-100 mg (1-2 ml), and then the daily dose is increased by 50 mg (1 ml) and adjusted to 300-400 mg (6-8 ml) per day once. Treatment is carried out in courses of 12-15 days.
Other indications: the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 50-100 mg (1-2 ml) for 1-2 injections.
Children
Hypovitaminosis B 6: the doctor prescribes the dose of the drug individually at the rate of 1-2 mg / kg of body weight per day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
Pyridoxine fissure convulsions: the drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously in a dose of 50-100 mg (1-2 ml) per day. Enter at a rate of 50 mg / min. Maximum doses for children have not been established.
Overdose of isoniazid preparations: for every 1 g of overdose, 1 g (20 ml) of pyridoxine is administered. If the dose of isoniazid is unknown, pyridoxine is administered at the rate of 70 mg / kg body weight. The maximum dose is 5 g (100 ml).
Adverse reactions
When using the drug, the following adverse reactions are possible:
on the part of the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, pain in the region of the heart;
on the part of the central and peripheral nervous system: headache, dizziness, drowsiness, agitation, incoordination, paresthesia, numbness in the extremities, the appearance of a sensation of compression in the extremities is a symptom of “stockings and gloves”, loss of consciousness and development by the court with the rapid introduction;
part of the respiratory system: difficulty breathing;
from the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, increased gastric secretion;
metabolism: reduced folic acid levels
on the part of the immune system, skin and subcutaneous tissue: anaphylactic shock, urticaria, rash, itching, skin flushing, dermatitis, angioedema, photosensitization;
Reproductive system and mammary glands: lactation suppression in the lactogenic period (sometimes used for therapeutic effect)
violations at the site of introduction of changes at the site of administration, including hyperemia, itching, burning at the injection site
general disorders: weakness, fever.
Overdose
Symptoms: increased side effects, metabolic disorders of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids; degenerative changes in the central nervous system (peripheral neuropathy) and parenchymal organs (metabolic disturbances associated with a significant decrease in the activity of nicotinamide coenzymes NAD and NADP and a deficiency of nicotinic acid).
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy: hyperparesthesia, paresthesia, muscle weakness. Sensory neuropathies with progressive gait disturbance, numbness and tingling in the legs and arms, partial baldness, reduced body resistance to infections, reduced activity of the anticoagulant system are possible. With prolonged use in large doses, hypervitaminosis B 6 develops, which is characterized by a sharp decrease in the protein content in the muscle tissue and internal organs. In the early stages of hypervitaminosis In 6 skin rash, dizziness, convulsions may appear. With the abolition of the drug, these symptoms disappear.
Treatment. Removal of the drug, symptomatic treatment.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The drug is prescribed during pregnancy during toxemia of pregnant women and with vomiting in pregnant women. In the appointment of the drug during lactation may inhibit lactation.
Children
The drug is used in pediatric practice. Enter intramuscularly and intravenously. Doses and mode of administration depend on the pathology (see Section "Dosage and administration").
Features of the application.
Use with caution in patients with gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer in history (due to a possible increase in the acidity of gastric juice), with functional liver failure (pyridoxine in large doses may impair its function).
Pyridoxine metabolism is impaired with regular use of alcohol.
May cause false positive for urobilinogen using Ehrlich reagent.
The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving motor transport or other mechanisms
During treatment, care should be taken when driving and working with mechanisms in connection with the possibility of the development of side effects from the nervous system.
Interaction
Diuretics - when combined with pyridoxine, the effect of diuretics is enhanced.
Hormonal contraceptives, cycloserine, penicillamine, isoniazid, hydralazine sulfate, ethionamide, immunosuppressants - when combined with pyridoxine, the effect of the latter is weakened.
Sleeping pills and sedatives - when combined with pyridoxine, the hypnotic effect is reduced.
Anti-parkinsonic drugs - when combined with pyridoxine, the effectiveness of agents for the treatment of Parkinson's disease is reduced.
Phenytoin - when combined with pyridoxine, the effect of phenytoin is reduced.
Corticosteroids - when combined with pyridoxine, the amount of vitamin B 6 in the body is reduced.
Glutamic acid, asparkam - when combined with pyridoxine, resistance to hypoxia increases.
Cardiac glycosides - when combined with pyridoxine, the synthesis of contractile proteins in the myocardium increases.
Tricyclic antidepressants - when combined with pyridoxine, the latter eliminates the side effects of tricyclic antidepressants associated with their anticholinergic activity (dry mouth, urinary retention).
Drugs of chloramphenicol of resorptive action - when combined with pyridoxine, the latter prevents ophthalmic complications that occur with prolonged use of drugs of chloramphenicol of resorptive action (synthomycin, chloramphenicol).
Pharmacodynamics
Pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B 6) is found in plants and animal organs, especially in unrefined cereal grains, vegetables, meat, fish, milk, cod liver and cattle, and egg yolk.
Quite a lot of vitamin B 6 in yeast. The need for vitamin B 6 is satisfied with food; partly it is also synthesized by intestinal microflora.
It plays an important role in the metabolism, is necessary for the normal functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system, and participates in the synthesis of neurotransmitters. In the phosphorylated form, it provides the processes of decarboxylation, transamination, deamination of amino acids, participates in the synthesis of protein, enzymes, hemoglobin, prostaglandins, the metabolism of serotonin, catecholamines, glutamic acid, GABA, histomas of the region, improves the use of unsaturated fatty acids, reduces cholesterol and lipids in the blood, improves myocardial contractility, promotes the conversion of folic acid into its active form, stimulates hematopoiesis. With atherosclerosis, vitamin 6 improves lipid metabolism.
Pyridoxine in atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus reduces the content of glycosylated hemoglobin, in addition, pyridoxine acts as a diuretic: it helps reduce high blood pressure.
It has been established that pyridoxine has a positive effect on the production of norepinephrine and serotonin, increasing their production during depressions, which is associated with its participation as a dof-decarboxylase cofactor in the process of catecholamine synthesis.
Pyridoxine can prolong clotting time and inhibit platelet aggregation, due to the binding of pyridoxal phosphate with fibrinogen and with specific amino groups on the surface of platelets.
Pharmacokinetics
Metabolized in the liver to form pharmacologically active metabolites (pyridoxal phosphate and pyridoxamine phosphate). Pyridoxal phosphate with plasma proteins by 90%. It penetrates well into all tissues. It accumulates mainly in the liver, less - in the muscles and central nervous system. Penetrates through the placenta, is displayed in breast milk. The half-life (T 1/2) is 15-20 days. Excreted by the kidneys (when administered intravenously - with bile (2%)), as well as during hemodialysis.
Basic physical and chemical properties
transparent colorless or slightly colored liquid.
Incompatibility
Do not mix a solution of pyridoxine in the same syringe with a solution of thiamine (vitamin 1), a solution of cyanocobalamin (vitamin 12), alkaline solutions, iron salts and solutions of oxidizing agents. Pyridoxine injections should preferably be done no earlier than 12:00 after thiamine injection.
It is not recommended to mix in the same infusion system or in the same syringe with the following drugs: adrenomimetics, ampicillin sodium salt, amphotericin B, ascorbic acid, other B vitamins, phytomenaion, dipyridamole, sodium oxypheriscorbone, phenothiazine derivatives (chlorpromazine azine, chloropromidine derivatives, chloromethyne resin, oxyphericorbon sodium, phenothiazine derivatives; aminophilin
Storage conditions
Shelf life - 3 years.
Keep out of the reach of children in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Do not freeze.
Terms of sell
You can buy Pyridoxine hydrochloride without a prescription.