Self-treatment of spinal hernia. How not to hurt yourself?
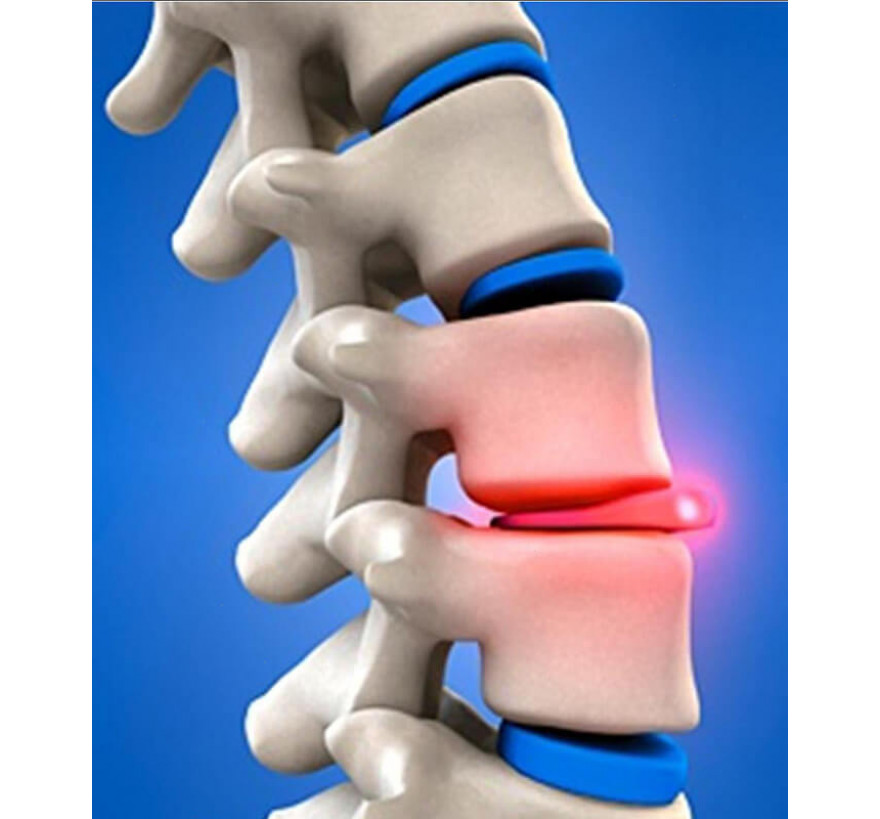
Herniated
intervertebral discs are one of the most common and most unpleasant
complications of osteochondrosis. Squeezing of the nerve roots with
hernial formations at first causes a strong pain syndrome, which
eventually subsides or goes away completely.
Further
manifestations of the disease are accompanied by a loss of sensitivity
of the limbs, a breakdown of the internal organs, a temporary or
complete loss of motor ability, etc.
The causes of the disease
In
the normal development of the body, the growth of the spinal column
occurs up to 25-30 years. After this period, the activation of
metabolism is somewhat reduced and there is a significant deterioration
in the nutrition of the tissues not only of the spine, but also of the
whole organism.
At about the same age, young people no longer
actively engage in sports and lead a more relaxed lifestyle. This,
together with bad habits, is the impetus for the thinning of the
intervertebral discs and the development of other diseases of the spine
(scoliosis, osteoporosis, sciatica, neuralgia, protrusion of the discs,
etc.).
Physically hard work, long-lasting sports injuries or
newly acquired ones gradually affect the elasticity of the spine and
increase the risk of disc herniation. There is a chance to replenish the
risk group and people who are overweight, lead a sedentary lifestyle,
or vice versa, exhausting themselves too active in sports.
Clinical signs of the disease
The
main danger of this disease is that severe pain syndromes are felt
already at the acute stage of the disease. At the initial pores, the
patient practically does not feel any discomfort, in some cases there is
only a slight stiffness and limitation in muscle movements, aching pain
after exercise or after a long stay in a static uncomfortable position.
Sometimes painful sensations occur during sharp turns or lifting, but
usually do not attach much importance.
The manifestation of the
disease in the following stages is expressed in the feeling of weakness
in the limbs, a certain loss of sensitivity and already stronger pain
syndromes during sudden movements of the body. Conventionally, the
development of the disease can be divided into two stages:
Pain in the back, especially directly in the spine.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the structure of the fibrous ring
lead to its cracking and decrease in strength. Then begins the
protrusion of the pulpal nucleus, which often causes swelling of
adjacent tissues and the formation of adhesions. When neoplasms reach
the nerve roots, an acute pain syndrome arises.
At the next
stage, the nature of the pain syndrome changes somewhat. Acute pain
turns into chronic dullness, but squeezing and affecting the nerve roots
cause their inflammation, which causes clinical signs in the
extremities (loss of sensation, numbness, weakness, or vice versa).
Symptoms of the disease

As
we have said, in the early stages it is extremely difficult to
recognize and diagnose a hernia of intervertebral discs, as well as
osteochondrosis, due to the absence of clinical manifestations. Patients
usually go to the doctor with complaints of back pain, stiffness of
motor functions, weakness of muscles and limbs, headaches, dizziness,
impaired vision and hearing, etc.
The doctor, in addition to the
main outpatient studies, may offer the patient to undergo MRI (magnetic
resonance imaging), CT (computed tomography) or x-rays. All images will
visualize dystrophic changes of the spine or the pathology of its
elements, which will help to finally establish the diagnosis and begin
the correct treatment. Even if the hernia of vertebral discs was not
established on the study, and only the initial stage of osteochondrosis
was noted, it is still necessary to undergo a course of treatment in
order not to start the disease.
Most often, hernia of
intervertebral discs occurs in the lumbosacral spine, affects the
cervical region a little less often, and most rarely occurs in the
thoracic region. In our country, spinal hernia is rarely treated with
surgery (only in especially critical situations when conservative
methods of treatment have not brought relief), while almost 50% of cases
abroad are treated with the help of operations.
Depending on which part of the spine the disease is located in, the symptoms of its manifestation will be different.
With the defeat of the cervical region are characteristic:
pains extending to the shoulders and upper limbs;
headaches and dizziness, sometimes to loss of consciousness;
sudden jumps in blood pressure;
numbness of the fingers of the upper limbs;
feeling cold in the upper limbs;
disorders of sleep, hearing, vision, psychological state, sometimes memory.
With the defeat of the thoracic is noted:
chronic pain in the sternum, especially after exercise or a long stay in an uncomfortable position;
thoracic pain syndrome, aggravated by scoliosis or kyphoscoliosis;
pain under the shoulder blades;
pains in the heart, especially with sudden movements of the body.
With the defeat of the lumbosacral are observed:
local pain in the lumbar region (lumbago), which increases even with low loads;
pains in the buttocks, the back of the thigh and lower leg;
feeling of weakness, numbness and tingling of the lower limbs;
sensation of coldness of the lower limbs;
failure of the organs located in the pelvic bones (urinary disturbance, potency, incontinence).
Treatment of herniated intervertebral discs
Patients
suffering from this disease must have patience during treatment. Full
recovery is possible, but subject to the implementation of all measures
and procedures prescribed by the doctor.
In some cases, pain
syndromes with herniated intervertebral discs subside after five to six
weeks. A period of remission begins, and surgery is not proposed. The
operation is carried out only as an extreme measure with the failure of
conservative treatment, which could not alleviate the pain syndrome, the
disease caused neurological complications. Or when compressing the
horse's tail (severe pain in the buttock, the back of the thigh with the
transition to the lower leg, cutting pains in the lower abdomen,
incontinence of feces and urine, weakening of potency).
Another
significant drawback of surgical intervention is the operative trauma
received by the patient when the hernia is removed through a
trephination incision. Nowadays, with the advent of surgical microscopes
and the development of microsurgical technologies, this hole is being
kept to a minimum in order to damage the surrounding inflamed tissue as
little as possible.
The basis of conservative treatment is drug
therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In many cases, a
method of blocking the pathological site using corticosteroids has
proven effective. As we have said, the pain passes with time, but this
does not mean that the disease is cured. During the first acute period,
the patient is prescribed a sparing regimen or, in particularly
difficult situations, bed rest.
The blockade quickly relieves pain,
muscle spasm, and, consequently, pinching of inflamed nerve roots. The
patient feels relieved, his motor ability returns, the movements become
more active and the person feels that he is ready for normal physical
exertion.
Often at this stage, patients think that the treatment
has already been completed (after all, relief has come), but this is
only a temporary effect. If you do not continue intensive therapy after
some time, the disease will manifest itself with a new force and may
lead to more negative consequences.
In some cases, the doctor may
prescribe an extension of the spine to reduce compression of the
trapped area. Often, this contributes to a more rapid recovery, but it
is not worthwhile to prescribe yourself a stretching procedure,
especially at home, as this process should be observed by the attending
physician. Otherwise, you risk aggravating the situation and cause new
injuries to the damaged spine.
Modern conservative methods of
treatment suggest the use of therapy with multifunctional electrodes,
treatment with shock wave therapy. In addition to the main purposes it
is recommended to carry out exercise therapy, general massages, manual
therapy of the spine, it is useful to do swimming. All additional
measures are aimed at restoring and strengthening the corset of the back
muscles, restoring elasticity and physical activity. After all, the
human body is unique and able to self-repair, the main thing is to
correctly direct it to recovery.
Self-treatment of spinal hernia
Some
patients, who do not particularly care for medical institutions, are
convinced that any diseases can be defeated at home on their own. This
also applies to herniated discs. Many reference books of traditional
medicine and information from the Internet convince that it is possible
to recover by performing some simple physical therapy exercises or
applying compresses of herbs.
Perhaps all these rubbing and
ointments with honey, onions, iodine, menthol or fortifying massages are
effective, but already in the period of recovery. At the first moment
of the onset of acute pain or the manifestation of other symptoms of the
disease is not recommended, and in some cases it is even strictly
forbidden to do massages.
At the first signs of illness (numbness
of the limbs, tingling in them, feelings of weakness in the muscles,
etc.), it is better to contact the doctor, who will order you to undergo
an MRI or CT scan, and, based on these results, will be able to
correctly diagnose.
Therefore, do not immediately rush to put
compresses, align the spine, lying on the floor for an hour and in no
case do not engage in self-stretching of the vertebrae. In this case,
all methods of traditional medicine are aimed at deep warming of soft
tissues and removal of pain syndromes, but they will not help you to get
rid of anxious illness.
Thus, with this disease, self-treatment
at home is generally not allowed, unless of course you have set yourself
the task of becoming an invalid, and further treatment with traditional
methods should be carried out as an additional to the main therapy,
under strict supervision of the attending physician and only with his
approval.
If you have a genetic predisposition to diseases of the
spine, but the main symptoms have not yet been observed, in order to
prevent, you can conduct courses of massages, physical therapy and other
healing activities. But for their own reassurance to people engaged in
heavy physical labor, former athletes and people who lead a low-active
lifestyle, doctors recommend at least once a year to undergo a medical
examination. It will be useful at any age for a real assessment of the
condition of your spine and the body as a whole.
And the rest, as
they say, "the matter of technology"! With the right and reasonable
attitude to your body, you will prolong its youth, physical fitness and
be healthy. Some tips for keeping your back and spine in working
condition:
try not to lift sharply weights (if it is
necessary, bend your knees, keeping your back straight, which will allow
you to evenly distribute the load on the spine);
try to avoid sharp turns or tilting of the body, especially when accompanied by weight lifting;
avoid drafts, do not overcool the back and the whole body;
lead an active lifestyle, especially if you have a sedentary job;
do prophylactic gymnastics, go to the gym, swim;
it is not necessary and much to exhaust the body with loads (they must be within reasonable limits);
Try to get rid of bad habits or at least reduce them to a minimum.
And
remember, hernia of intervertebral discs is not a sentence, it can
always be cured in the initial stages. And even with a completely
neglected version, with appropriate and proper treatment, one can remain
vigorous, able-bodied and enjoy life.
