Arthritis: what is it? Causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention
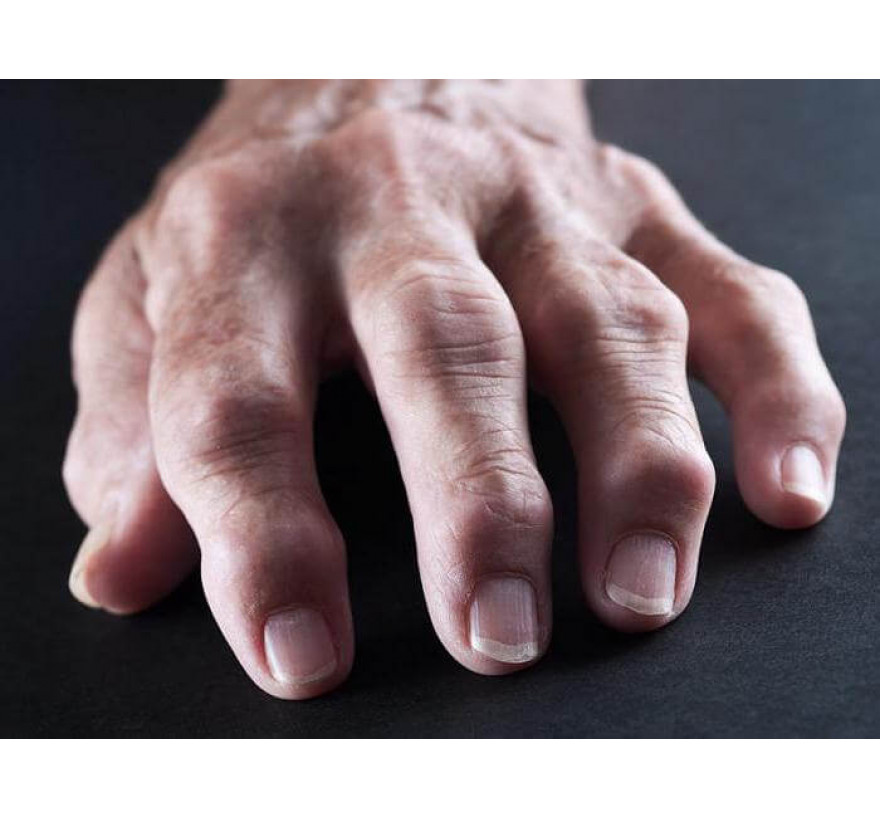
Difficult diagnosis and long treatment make arthritis of the joints one of the most serious illnesses. However, a large percentage of those cured, allows doctors to give a favorable prognosis.
Every sixth person becomes disabled. Meanwhile, the disease is easily preventable, diagnostics in the early stages ensures complete cure. One has only to reconsider their lifestyle and not to neglect the alarming symptoms.
Varieties of Arthritis
Practicing rheumatologists and orthopedists in their work use several classifications of inflammatory diseases of the joints. However, the most extensive is the classification, partly providing for the causes of this disease. According to which, arthritis is divided into major and secondary, (complications of other diseases).
The term “arthritis”, introduced by Hippocrates, was used in subsequent centuries to denote any articular pathology. Starting from the end of the 15th century, scientific medical luminaries began to gradually distinguish individual forms of the disease.
So, Bayu singled out rheumatism among arthritis. At the beginning of the 17th century, Sidengam described gout and rheumatoid arthritis as independent forms. Decades later, infectious specific arthritis was combined by Bouchard under the common name "Infectious Pseudorevmatism." In the 19th century, Muller made the first attempt to classify the pathology of the joints. He clearly distinguished inflammatory joint diseases (arthritis) from dystrophic (arthrosis). This division retains its value to the present.
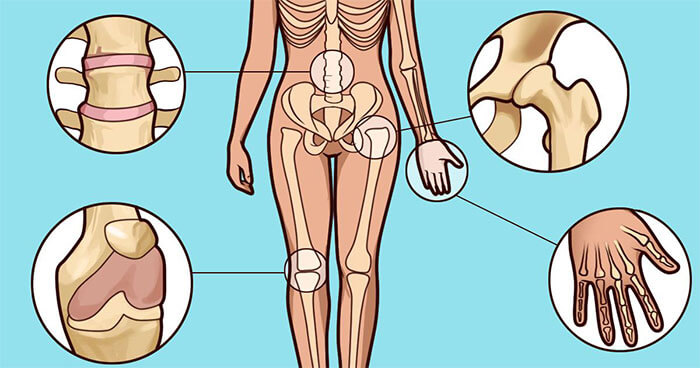
Primary forms
Osteoarthritis - affects the cartilage tissue of the joints, resulting in complete deformation.
Rheumatoid arthritis - a disease of the connective tissue, with the defeat of small joints.
Septic arthritis (infectious) - a fungal or bacterial infection affects large joints, knee or hip. Then all joints are involved in the inflammatory process.
Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by the growths of uric acid salts. A bump near the thumb is a manifestation of this type of arthritis.
Still's disease is a form of rheumatoid arthritis, very difficult to diagnose. In most cases, it is observed in children under the age of 16 years.
Spondylitis is an infection in the vertebrae, mainly due to bacteria. There are several forms of the disease - spinal osteomyelitis and tuberculous spondylitis.
Arthritis, a complication of other diseases
A separate diagnosis requires arthritis of the joints, developing a second time for other diseases, because in that case their symptoms come to the fore in this case.
For example, for systemic lupus erythematosus, in addition to the lesion of small joints, fever and the butterfly symptom are characteristic: reddening of the skin of the face in the cheeks and nose, shaped like butterfly wings.
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a disease of the connective tissue and its derivatives.
Purpura - small-spotted capillary hemorrhages in the skin, under the skin or in the mucous membranes.
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic, progressive joint disease that occurs during psoriasis.
Reactive arthritis is an inflammatory disease with damage to the joints that develops after the transfer of some infections (urinary, intestinal, nasopharyngeal).
Hemochromatosis is a hereditary, genetically determined disease, manifested by a violation of iron metabolism with its accumulation in tissues and organs.
Hepatitis is an inflammatory disease of the liver, usually of viral origin, often spreading to the joints.
Granulomatosis is an inflammation that is characterized by the formation of granulomas (nodules) resulting from the transformation of cells capable of phagocytosis.
Borreliosis is the most common tick-borne disease in the Northern Hemisphere. Bacteria are transmitted to humans by the bite of infected ticks. First of all, the locomotor system is affected.
Accurate classification greatly facilitates the correct diagnosis and further therapy.
Causes of disease
Arthritis is a complex and diverse disease. Its development is due to many reasons. In the medical classification, it is customary to distinguish several main groups:
Infectious provocateurs - the presence of viral and bacterial diseases.
Traumatic causes - the damaged joint was not fully restored, which further caused the inflammatory process.
Immunological factors - poor diet, lack of vitamins, bad habits, including the abuse of caffeinated beverages, increase the risk of disease.
Genetic predisposition. The disease can be inherited. If in the circle of next of kin there are people suffering from inflammation of the joints, then the chances of getting sick will increase.
A very wide range of people are at risk. In addition to the obvious reasons, there are circumstances that give a powerful impetus to the disease:
Female. Statistics show that women are much more likely than men to seek help from rheumatologists. This is a logical explanation. The natural, but difficult process of pregnancy and childbirth deprives the body of many beneficial vitamins and minerals. Childbearing is an increased load on the entire musculoskeletal system and possible complications in the form of arthritis diseases.
Chronic diseases.
Fractures, sprains, sprains and other injuries.
Surgery under general anesthesia.
Any types of allergies.
Vaccine complications.
Other diseases of the joints. For example, arthrosis, bursitis, Bequeira cyst almost always give complications.
Advanced age. Over time, the joints tend to wear out if you do not carry out a set of activities.
Summing up, it can be argued that anyone can be at risk, including young children.
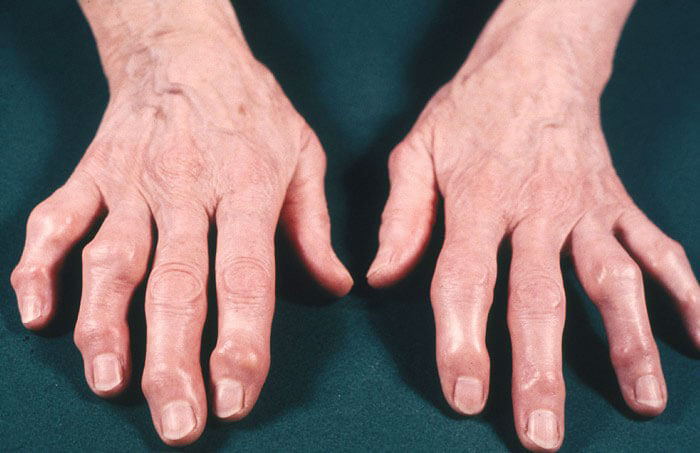
Symptomatology
The main indicator of the disease - pain in one or more joints. Many people do not take it seriously. Short discomfort does not cause any inconvenience. Unpleasant symptoms are quickly relieved by massage or by taking simple painkillers.
Over time, it becomes more difficult to ignore the symptoms. The pains intensify, acquire a wave-like character. When moving and at night the disease is exacerbated.
Obvious symptoms appear during this period:
Morning stiffness;
Puffiness with redness of the skin;
Increased temperature in the area of inflammation;
Limitation of mobility due to severe pain;
Noticeable to the naked eye the deformation of the joints.
Symptoms can be different, depending on the species. On the example of the most common diseases, you can create a general picture of the signs:
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by a symmetrical lesion of the joints, noticeable nodules appear at the bend sites. The exacerbation of the disease is observed in the early morning, by the second half of the day the symptoms almost disappear. If the disease is in the acute stage, the patient is severely feverish, the extremities become numb, severe pain appears during inhalation, lymph nodes grow, blinking is accompanied by sharp pain.
Reactive arthritis - against the background of common symptoms, there is inflammation of the urinary tract, the appearance of cystitis, urethritis. Increased tearing, cramps in the eyes, complications such as conjunctivitis.
Infectious - chills, fever, severe headaches, general weakness, swelling of tissues in the areas of the affected joints. The type of infection that provoked the disease is determined by means of tests.
Gouty - the joints of the arms and legs swell up. Most often affects the first joints of the big toes. But, gouty arthritis can appear in the elbows, in the knees, on the fingers. Places of inflammation turn red. Pain cramping - from very strong, twitching, to weak, spreading.
Psoriatic - small joints of the fingers and toes and hands increase in size, causing a general swelling of the limbs. It is not symmetrical, unlike rheumatoid. The skin of the affected fingers acquires a purple-bluish tinge, as after impact. Complete or partial lack of mobility. The pain is very strong. It is impossible to do without taking strong anesthetics.
Osteoarthritis - symptoms appear slowly, gradually, as the disease progresses. The first warning sign is the crunching of the limbs and the spine. Depending on the form of flow, it can be in the stage of regression for many years. Extremely dangerous small symptoms with a large scale lesions.
Traumatic - the inflammatory process makes itself felt by the appearance of a crunch in the damaged joints, as in osteoarthritis. Pain and swelling may not appear soon. Therefore, you should not ignore the primary signs.
Diagnostics
A large number of causes and symptoms make the diagnosis of arthritis of the joints challenging. Only an experienced and highly qualified doctor will be able to collect all the components of the disease into a single picture. If common species can be diagnosed quickly enough, then rare types caused by other chronic pathologies are difficult to detect. For example, rheumatoid arthritis of the joints, so far remains a mystery to rheumatologists - the causes of the appearance are not sufficiently substantiated.
To designate an effective course of therapy, the final diagnosis is made along with the root causes.
For this, a wide range of medical events is carried out:
Going full history of the disease;
Laboratory studies are conducted (total blood biochemistry, sugar level determination, PCR, urinalysis, etc.).
Infectious, allergic, traumatic, bacterial and other connections are excluded, until a provocative determination is made;
Research using diagnostic equipment - radiography, ultrasound, MRI;
Biopsy of the synovial fluid that fills the joint cavity.
Arthroscopy A more modern way to study the joints and the collection of synovial fluid. The method gives accurate data and, as a rule, does not require repeated procedures.
Compiled a complete clinical picture of the disease.
All sequential diagnostic steps are crucial for determining joint disease. Comprehensive hardware studies do not exclude, but complement each other.
As noted above, making a correct diagnosis is a difficult task. Therefore, it is impossible to ignore or replace any diagnostic methods. Therapy and further prognosis of the disease completely depends on this.
Arthritis treatment
Arthritis treatment takes place in several stages. Each of them, before the therapy, has its own goals and objectives, which are implemented using certain methods. If conservative, standard schemes are used at the initial stages, then at subsequent stages surgical intervention is already shown, up to the removal of the affected joints.
The goals of any therapy are the same:
Relieve pain;
Stop the progress of the disease;
Restore the joint;
Exclude possible complications.
To achieve results, apply:
Drug therapy. First of all, it is aimed at the removal of excruciating pain and the resumption of a normal lifestyle - sleep, work, movement, the implementation of daily activities. They prescribe anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs (for example, Diclofenac, Baralgin, Ketorol), which can not get rid of the disease, but eliminate the pain syndrome. Chondroprotectors that are able to repair cartilage tissue. Antibiotics of a different spectrum of action, for removal of a strong inflammation and abscess.
Physiotherapy activities. They include ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis with anesthetics, phonophoresis, massage, mud therapy, heating, wraps, hydromassage, therapeutic baths. Already after a week course, the patient's condition improves significantly. In combination with medical treatment, any type of arthritis becomes practically asymptomatic. The patient's quality of life is improving, and he can already begin his daily duties.
Physical therapy and balanced nutrition. Arthritis treatment requires a complete revision of the diet. A large number of fresh vegetables and fruits are mandatory, the fatty meat is replaced with fish and seafood, fried, salty, spicy dishes and all kinds of seasonings are completely excluded. All food is cooked and stewed without adding oil. Dietary nutrition will ensure the supply of essential minerals and vitamins in the body and, in particular, the affected joints.
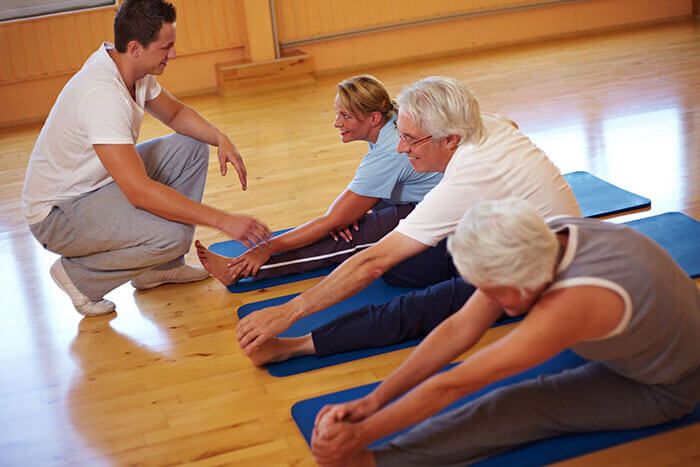

Physical activity is also subject to adjustment. The state of rest and constant bed rest only aggravate the patient's condition. Depending on the severity of the disease, exercise therapy is prescribed individually by the attending physician. The complex should be performed regularly, without gaps, taking into account all medical recommendations.
As an example, a number of exercises for ankle arthritis can be given:
smooth rolling from toe to heel;
walking on the inside of the foot;
jumping on the toes;
walking on the heels;
in a sitting position, stretching the toes towards oneself.
For severe cases, many exercises can be performed in the water, where the load is reduced and exercise therapy is more comfortable. Also shown using an exercise bike.
Therapeutic massage reduces tension and swelling of the joints. Be sure to be included in the overall process of treating arthritis. A visit to a sanatorium will help to achieve maximum results.
In any case, all therapeutic measures, physical therapy exercises and medical drugs are prescribed only by the attending physician, based on the diagnosis.
Folk Arthritis Treatments
In the fight against the disease all the ways are good. Traditional medicine offers many recipes tested by no one person. The most popular ones are:
Coniferous baths. Spruce branches pour boiling water, insist 10 minutes, lower the legs in a container with pine needles for 30 minutes. After the procedure, immediately go to bed. Can be repeated daily, until relief.
Heat flax seeds in an oven or in a dry frying pan, place in a fabric bag and apply to the sore joint.
Fresh cabbage is famous for its anti-inflammatory effects. Warm sheets applied to arthritic affected areas, pre-lubricated with any kind of honey. Wrap the wrap with cling film and a warm scarf. It is advisable to do this at night.
Mix a raw chicken egg with two tablespoons of table salt, apply the composition on a clean cotton fabric and wrap a sore spot. As it dries, apply a new batch of the mixture.
Kefir mixed with crushed chalk to a thick cream. Compress set for the night. Relief is not long in coming.
Despite the effectiveness of folk methods, it should be remembered that self-treatment can end very badly. Without traditional methods, a positive result will be temporary, and arthritis will return very soon.
The combination of several techniques, traditional and traditional medicine gives a stable, long-lasting effect and reduces the risk of relapse.
Prevention
The prognosis for all types of arthritis is generally favorable. In most cases, the disease is completely curable within 6-9 months. During this period, it is important not to abandon a full-fledged life, but to adapt to it as much as possible. The implementation of simple recommendations and rules will improve the overall condition of the patient:
Reduce the load on the joints;
Perform stretching exercises;
Strict implementation of all recommendations of the attending physician;
Full sleep;
Dieting is a balanced diet.
Health is totally dependent on self-control and compliance. This is a small price for a complete cure for arthritis. It is only important to adhere to preventive measures to prevent recurrence.
A healthy and proper diet should be a good habit for life. This will help not only prevent the return of arthritis, but also have a positive effect on the general condition of the body.
Completely exclude alcohol and smoking. Bad habits have never contributed to good health.
Avoid infectious diseases. To do this, take immunomodulatory drugs and thoroughly treat even a runny nose.
To live an active lifestyle. Long walks, feasible sports should be a daily responsibility.
Avoid heavy physical exertion to minimize the risk of injury.
Before bed do preventive massage.
Only by completely revising your lifestyle can you avoid relapse and prevent the development of arthritis with a new force. If the disease has returned, to disregard even the seemingly insignificant symptoms is a direct path to the surgical table and possible disability.
