Rubella
Causes of rubella infection
The virus continues to secrete for 5-7 days after the appearance of rashes. A child with congenital rubella secretes the virus for a longer time (up to 20 months).
The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets. In pregnant women, a transplacental route of transmission to the embryo and fetus is possible.
Infection susceptibility in children without rubella immunity is high. In the first months of life, children do not get rubella, as they receive antibodies from their mother. Immunity in a sick person is established persistent, lifelong.
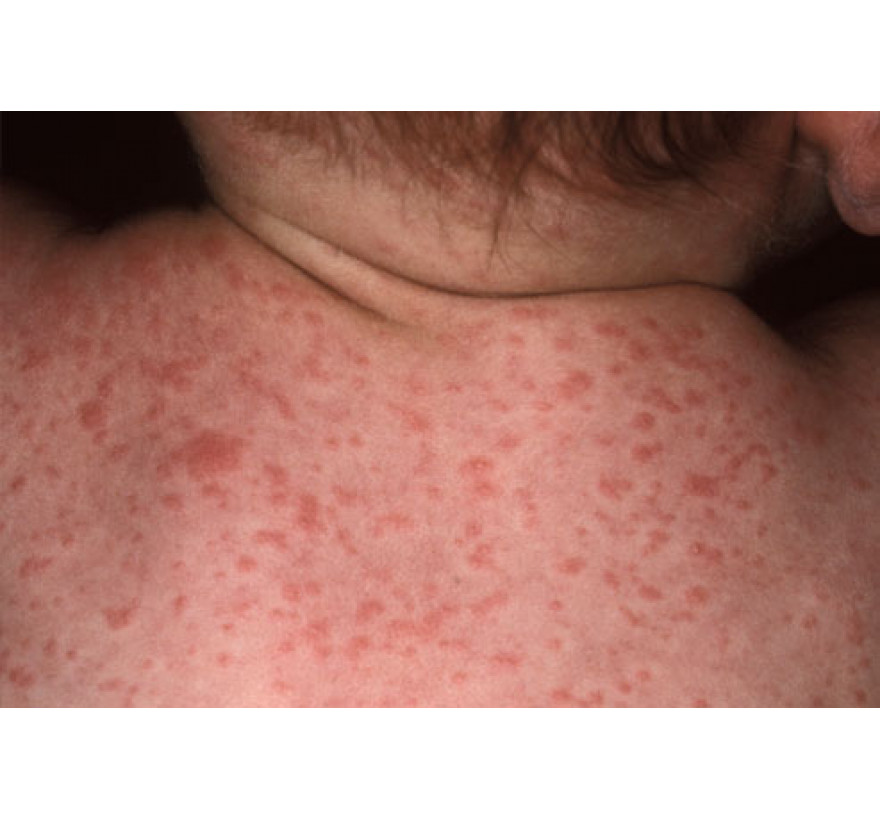
Rubella symptoms
The incubation period lasts 11-21 days, prodromal - 0-1 days, the height of the disease and the rash period - 4-6 days, convalescence (recovery) - 1-2 weeks.
Rubella virus enters the child's body through the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and first multiplies in the lymph nodes, causing their increase. From there, after a week it enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body. After the manifestation of the rash, the virus disappears from the blood in a week.
Usually there is an increase in the occipital and posterior cervical lymph nodes. They increase 1-2 days before the appearance of the rash or already against the background of rashes. Their sizes reach 1-2 cm in diameter. The nodes, as a rule, are densely elastic in consistency, moderately painful, not welded together.
From the first day of the disease, a rash characteristic of rubella occurs on the skin. The rash is small-spotted, it is spotty-papular, pink in size with sizes from 3 to 5 mm. Elements of the rash do not merge and do not leave pigmentation. Rash occurs simultaneously, as a rule, in one day. Additional rashes are rare. Rashes can be found on the entire surface of the body, but more often they are localized on the face (in particular in the region of the nasolabial triangle), on the back, buttocks, extensor surfaces of the arms and legs. Sometimes, simultaneously with a rash on the skin, small single rashes appear on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Such elements of the rash persist for 1-4 days, and then disappear without a trace.
The general condition of the child, as a rule, is not disturbed, and rubella usually proceeds in a mild form. Intoxication, fever and catarrhal phenomena are mild. Although a runny nose, dry cough, sore throat, and lacrimation can sometimes occur.
More severe forms of rubella with severe intoxication are observed while occurring with other infectious diseases - influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, and tonsillitis.
Rubella is diagnosed based on the clinical picture and laboratory data.
Recovery does not occur until the fifth day of illness, after the disappearance of all symptoms of the disease and in the absence of complications.
Rubella Complications
Rubella complications are rare. Specific - arthritis and encephalitis. The most dangerous complication is rubella meningoencephalitis with severe gross residual effects. In this case, a fatal outcome is possible.
Rubella during pregnancy
Rubella is very dangerous during pregnancy, especially in the early stages (up to 18 weeks), due to the high risk of developing congenital rubella in the embryo and the fetus, and as a result, the development of gross malformations.
Rubella virus, causing mild rubella in a pregnant woman, has a rude effect on the developing embryo. A child can be born with gross congenital malformations with the so-called Gregg triad, which includes: complete deafness of the child, blindness and congenital heart defects. The disease of a woman with rubella in the second half of pregnancy, closer to childbirth, does not pose a great danger to the development and life of a future person. A baby can simply be born with a typical rubella rash.
Rubella Prevention
For the prevention of rubella, children are currently vaccinated (vaccinated) at the age of 12-14 months and again at 6 years of age. Rubella vaccination is also given to girls aged 13 years who have not had rubella before, and women planning a pregnancy no later than 3 months before the planned pregnancy (in the event that they have not had rubella before). After immunization, specific immunity develops in almost 100% of vaccinees after 15-20 days.
Rubella treatment at home
Treatment is usually done at home. Hospitalization in an infectious diseases hospital is necessary only in case of complications.
The room where the rubella patient is located must often be ventilated and wet cleaned in it.
It is necessary to observe bed rest for 4-5 days, a dairy-vegetable diet enriched with vitamins, heavy drinking.
With traditional treatment, vitamin complexes are prescribed, ascorutin (vitamin C) is required. General-strengthening and strengthening the immune system remedies are also prescribed. There is no special treatment (etiotropic).
Children who have had rubella encephalitis need to be followed by a neurologist for two years after recovery.
Alternative treatment of rubella folk remedies
Phytotherapy. Vitamin C, which is necessary for the body, is especially increased in need during illness, is found in large quantities in rose hips, blackcurrant and strawberry berries, onion and dill. An important vitamin P is found in grapes in green tea. You need to try to actively consume these products.
It is good to make vitamin teas. For example, from rose hips and blackcurrant berries in a ratio of 1: 1; or rose hips and lingonberries 1: 1; or rose hips, lingonberries and nettle leaves in a ratio of 3: 1: 3, respectively. Brew the ingredients in boiling water and take as tea 2-3 times a day.
When a skin rash appears, a rosehip broth, coltsfoot, calendula, cornflower, and chamomile are used. With a rash, an infusion of leaves and flowers of celandine can be used for baths and washing the skin. To do this, pour 4 tablespoons of chopped grass with 6 cups of boiling water, insist in a sealed container for 1 hour, strain.
The herbs of edelweiss, valerian, motherwort have a calming effect, are used as a decoction. After its preparation, the herbal collection must be insisted for a long time (within 10 hours) in a thermos to maintain a certain temperature. Children from 1 to 3 years old take 1 tsp. 1/2 liter of liquid, from three to ten years - up to 1 tbsp. l., from ten years and older, as well as adults - 2 tbsp. l Drink an infusion of 100-150 ml before meals 3-4 times a day. To improve the taste in the infusion, you can add sugar, honey or jam.
With rubella, ready-made pharmacy fees are also used, consisting of birch buds, a string of clover flowers, dandelion root, wormwood grass, yarrow in an equal ratio of 1/3 cup 3-4 times a day.
Birch buds have an antipruritic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, positively affect the metabolism, accelerate the excretion of decay products harmful to the body.
The recipe for another decoction. You need 1 tablespoon of berries and leaves of lingonberry, St. John's wort grass. Pour the crushed ingredients with 3 cups of hot water, simmer for 10 minutes, insist 1 hour, strain. Take 0.25 cups 4 times a day.
