What is candidiasis
Among the many common causes that are the trigger for the occurrence of thrush, the following can be distinguished:
taking antibacterial drugs;
overwork;
stressful situations;
mucosal injury;
a sharp change in climatic conditions;
unbalanced diet, the predominance of simple carbohydrates;
diabetes;
violation of the functional activity of the endocrine glands.
For each type of pathology, there are specific provocative factors.
So, the cause of urogenital thrush in women can be wearing narrow synthetic underwear, abuse of means for intimate hygiene, hormonal disorders. And damage to the nail plate may appear as a result of prolonged exposure of the hands or feet to dampness.
Forms and types of candidiasis
There are three forms of candidiasis:
Sharp. It is manifested by pronounced signs.
Chronic It is characterized by a change in periods of remission and relapse (of varying intensity).
Carriage The fungus is detected as a result of diagnosis, but there are no signs of pathology. The treatment is not carried out.
Depending on the location of the affected tissues, several types of thrush are distinguished:
urogenital;
skin, nails, feet, palms;
lungs and other internal organs;
gastrointestinal thrush;
the oral cavity;
ears, eyes and so on.
Urogenital
The urogenital type of the disease affects the mucous membrane and skin of the genitals and urinary tract. When diagnosing a disease in a pregnant woman, a child is often born with signs of thrush. Transmission occurs during intercourse.
Most often, the symptoms of the urogenital species are fully manifested in women, and men are carriers. However, males are also susceptible to pathology, while the fungus can spread to the prostate gland.
Oral candidiasis
The development of thrush of the oral cavity is most often diagnosed in young children. The main reason is the presence of fungus in the birth canal of the mother. In adults, in addition to the above factors, improper prosthetics can cause candida growth.
As a rule, the disease proceeds in an acute form with vivid intense symptoms. The lesion can be localized on the surface of the tongue, gums, lips and other individual areas. In the absence of timely treatment, the fungus quickly spreads to neighboring areas - a total lesion develops. If the disease takes on a chronic form, the infection penetrates the tissues of the nasal passages, vocal cords, and upper gastrointestinal tract.
Candidiasis of the skin, nails and feet
The main localization of fungal skin lesions is palms and folds (in the groin, under the armpits, under the chest, between the fingers, buttocks). In children, the infection can invade smooth skin. The fungus quickly spreads to neighboring areas, forming extensive foci of dark red or burgundy color. Inflammation of the nail leads to the fact that the plate becomes thin or, conversely, thickened, crumbles, and the nail roll peels off and swells.
The reproduction of candida on the palms, feet and nails is associated with their prolonged exposure to high humidity. Pathology can occur for many years in a chronic form, exacerbating in the form of inflammation. The most intense signs of candidiasis of the skin appear in autumn and spring.
GIT candidiasis
The main reason for the candida's reproduction in the gastrointestinal tract is the uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs, especially against the background of a weakened immune defense. This type of thrush is one of the most common, it can be represented by a penetrating and non-penetrating form.
In the first case, the inflammation is characterized by a severe course, and can spread to the entire intestine or in places where there are already any disorders (for example, ulcerative formations). Non-penetrating candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract is a type of dysbiosis with a characteristic clinical picture: increased gas formation, impaired digestion of the food mass, pain, and the release of toxins into the blood.
Pulmonary form
Pulmonary candidiasis is of secondary origin. The disease is the result of inflammatory processes in the respiratory system, purulent infections, tuberculosis. The fungus can also spread into the mucous membrane of the bronchi. The disease is difficult to diagnose.
Candidiasis of the eyes and ears
Candida can even damage the tissues of the eyes and ears. In the first case, the cause of infection (in addition to the above) can be the wearing of contact lenses, eye injury, an allergic reaction. Symptoms are manifested in the form of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis and other pathologies. With increased secretion of the lacrimal glands or the appearance of sensitivity to light, you need to urgently consult a doctor, since the rapid development of a fungal infection can lead to blindness.
If there is a chronic history of otitis media, improper hygiene of the ear canal, and injuries, candidiasis of the ear develops.
The same can happen with prolonged local use of medicinal solutions containing corticosteroid components, water entering the middle ear, and high atmospheric pressure. The disease is characterized by a severe course, especially in childhood.
Symptoms of candidiasis
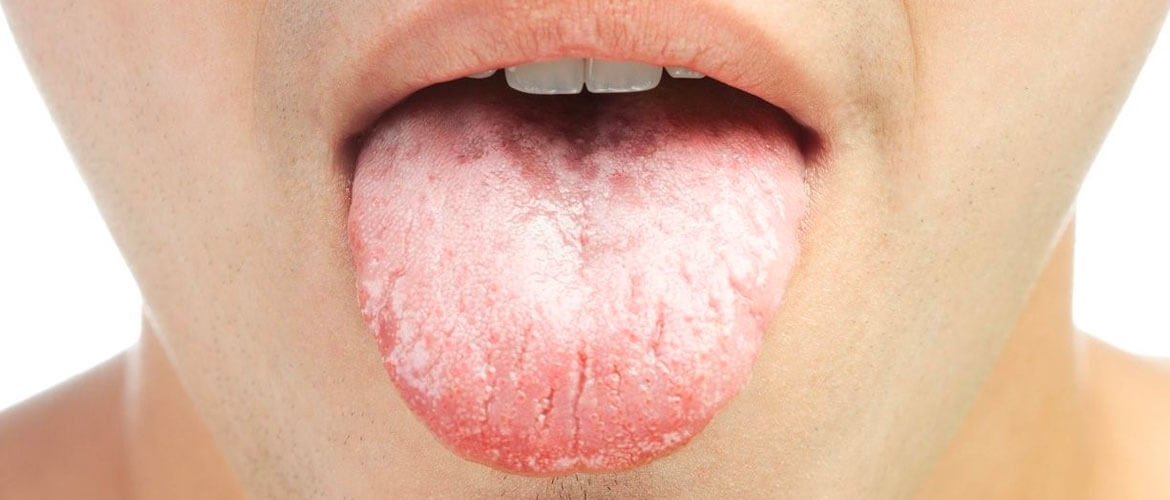
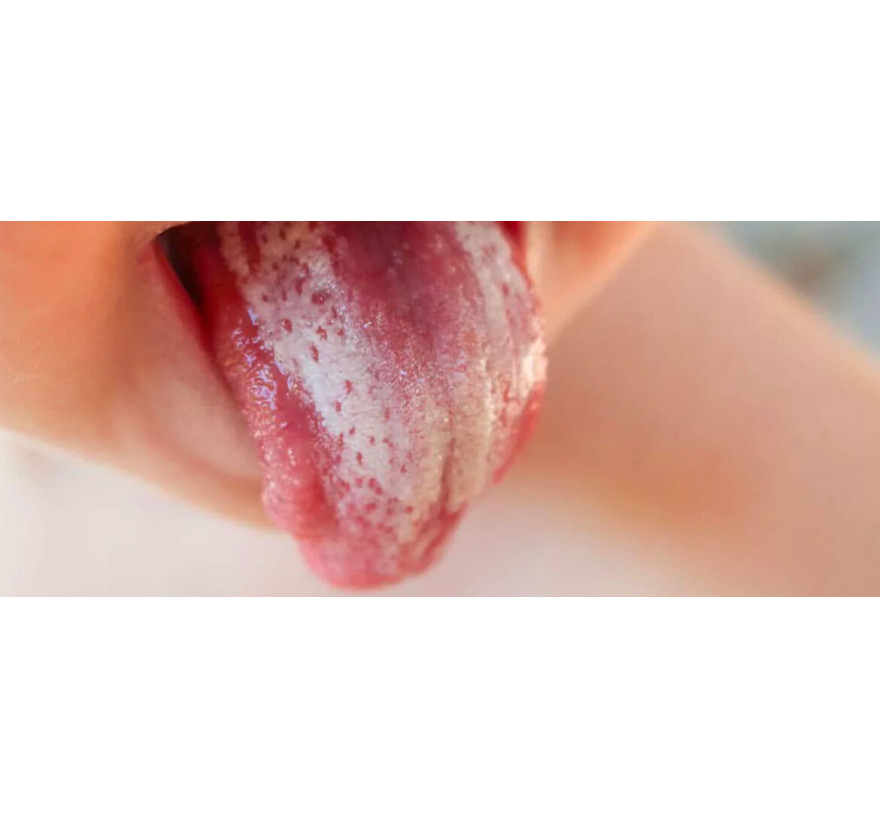
Oral cavity
dots, whitish plaques;
hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
bleeding sores, covered with white coating;
discomfort during eating;
swelling of the tongue, tonsils, lips.
Lungs
cough;
weakness, malaise;
sputum with an admixture of pus;
voice disorders;
pain in the respiratory system;
temperature increase.
Genitourinary organs
white, curdled discharge;
hyperemia of the skin and mucous membranes;
genital plaque in the form of a film;
itching
swelling of the mucous membrane;
burning sensation during urination;
discomfort during intercourse and urine output.
An ear
discharge of a white or grayish tint;
severe itchy sensations;
weeping ulcerations on the skin of the ear canal.
Skin
white layers in the form of crumbs on the affected area;
cracks;
vesicles;
peeling;
hyperemia;
itching
Nails
pustules in the area of the nail roller;
swelling and hyperemia of soft tissues;
brown shade of the plate;
stripes, tubercles on the nail;
thinning of the nail;
stratification, crumbling of the nail plate.
Eyes
increased lacrimation;
itching
vasodilation;
milk coating on the eyelids and eyeball;
vision disorder;
purulent discharge;
foreign body feeling.
Gastrointestinal tract
vomiting
lack of appetite;
pain behind the sternum;
violation of swallowing;
fever, chills;
weight loss;
increased gas production;
diarrhea;
mucus in vomit and feces;
itching around the anus.
Diagnostics

The diagnosis of candidiasis, its form and type begins with a visual examination in the doctor’s office. The specialist determines the degree of spread of fungal infection, notes the severity of symptoms, conducts a survey, takes material (scraping, smear) for subsequent laboratory research.
Laboratory diagnostics is carried out using the following methods:
microscopic analysis of plaque or discharge;
culture sowing;
enzyme immunoassay;
polymerase chain reaction.
Most often, to establish a diagnosis, they resort to examining the taken material under a microscope. ELISA, and especially PCR, is used in rare cases, since they are considered uninformative in relation to Candida fungus.
Candidiasis Treatment
Candidiasis treatment is carried out comprehensively, using local and / or systemic tools and methods. If the disease is of a secondary nature, the main pathology is simultaneously treated. The acute and chronic form of thrush is treated with different therapeutic regimens.
With not very pronounced symptoms, the use of local drugs in the form of ointment or cream is indicated. Among them should be noted: Clotrimazole, Natamycin.
In case of thrush of the oral cavity, rinses with chlorhexidine, aniline dyes are prescribed. In addition, it is permissible to lubricate the oral mucosa with a cream containing antimycotic components. In severe cases, the intake of antifungal agents is indicated.
Among the treatment methods used for the urogenital type of the disease, baths and douching (for example, with potassium permanganate), vaginal tablets and suppositories are most often used. The composition of medicines includes: clotrimazole, ketonazole and other compounds with an antifungal effect.
With extensive distribution, lack of effect from the use of local methods and means, pronounced symptoms and severe course, systemic therapy is indicated.
The most effective drugs in such cases are those containing fluconazole and itraconazole. As additional therapeutic measures, the appointment of vitamin complexes and the increase in the body's defenses by any available means can be noted.
Treatment in children
Thrush in newborns and infants, in most cases, proceeds without complications. For treatment, local tools and methods are used.
The most common, simple but effective procedure is the treatment of affected areas with soda solution. It is prepared based on: take a teaspoon of soda in a glass of boiled water at room temperature. Manipulations are carried out several times a day, cleaning the mucous membrane (or skin) from secretions with a tampon. Iodinol or nystatin drops are used in the same way.
If the skin is damaged after plaque is removed, ointments with anti-mycotic effect are applied to the infectious foci. The drugs of choice are agents containing nystatin, imidazole.
Medications for internal use are prescribed taking into account age restrictions, the severity of symptoms. In parallel, it is necessary to increase the immunity of the child, to ensure proper balanced nutrition.
With any form of therapy, its completion is possible only after the diagnosis and permission of the doctor. Even with a significant improvement in the condition, you should not spontaneously interrupt the course of treatment, otherwise the disease can take a chronic course.
Possible complications of the disease
If candidiasis therapy was carried out in a timely manner, negative health effects do not occur. A neglected disease, a chronic course of thrush is dangerous with numerous complications. For example, with an urogenital variety of pathology, the development of diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, organs of the reproductive system, and infertility is possible. In men, candidiasis can provoke prostatitis and urethritis, in women - erosive changes in the epithelium of the cervix, ovarian inflammation, vaginal stenosis, rupture of the fetal membrane and termination of pregnancy.
A complication of ear candidiasis can be sepsis, hearing loss. With ocular localization of the infectious process, the risk of visual impairment, blindness increases. In the case of candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract, negative consequences include peritonitis, internal bleeding, anemia, and others.
To prevent the development of candidiasis, it is necessary to carefully monitor the lifestyle, increase resistance to infectious influences and stresses. Periodic intake of vitamin complexes, hardening, a properly composed diet and timely access to a doctor are the main measures for the prevention of thrush at any age.
